Ganoderic Acid Lessens Alcohol/Medication-induced Liver Injury
- Categories:Media Center
- Time of issue:2024-03-21 15:43
- Views:
Ganoderic Acid Lessens Alcohol/Medication-induced Liver Injury
- Categories:Media Center
- Time of issue:2024-03-21 15:43
- Views:
Today marks the 24th "National Liver Day," a day when we pay extra attention to liver health. Excessive alcohol consumption, medication use, late nights, and emotional stress can all cause varying degrees of liver injury. Currently, research on how Ganoderma lucidum (Reishi mushroom) assists in protecting the liver is well-established. It can be said that those who consume Reishi daily silently benefit their liver. The article shared today is an informative piece by Taiwanese author Wu Tingyao, published on the GanoHerb platform in 2022. Even now, its insights remain relevant. The article delves into the active ingredients of Reishi for liver protection. Let’s revisit it together.

Many individuals not only have three meals a day but also consume medication and engage in social drinking. If you happen to be one of these people, you should seriously consider adding "Reishi alcohol extract rich in triterpene acids" to your daily regimen. This can provide protective effects for your hardworking liver, which tirelessly detoxifies. Research published in the "Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy" by Professors Xu Jianhua and Li Peng from Fujian Medical University highlights that the triterpene acids in Reishi alcohol extract can simultaneously mitigate injury caused by chemicals and alcohol to liver cells. Their mechanism of action is closely related to antioxidant properties.
In the experimental study, researchers used Reishi medicinal material provided by Fujian Xianzhilou Biological Science and Technology Co., Ltd. The material was identified by Professor Zhang Yonghong of the School of Pharmacy at Fujian Medical University as the fruiting body of Ganoderma lucidum. After pulverizing the Reishi material, they extracted the "Ganoderma Triterpene Acids (GTA)" using ethanol. The GTA was administered to mice in low, medium, and high doses (0.5, 1.0, or 2.0 g/kg) once daily for seven consecutive days. Within 2 hours after consuming GTA on the 7th day, the mice were intraperitoneally injected with 56% Red Star Erguotou Baijiu or carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) to induce acute liver injury. The researchers analyzed liver injury in the mice 16 hours later and compared it with normal mice (blank control group), untreated mice with acute hepatitis (model control group), and mice treated with antiviral drugs for hepatitis (Bifendate group).
Discovery 1: With GTA protection, hepatic indicators are lower.
The inflammatory response triggered by Baijiu and carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) damages liver cells, causing enzymes originally contained within the liver cells to leak into the bloodstream. This leads to elevated serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST). However, in mice pre-treated with high doses of GTA, although these two liver inflammation markers still increase, the magnitude of elevation is significantly reduced. This demonstrates that GTA can safeguard liver cells and mitigate the damage caused by Baijiu and CCl4.
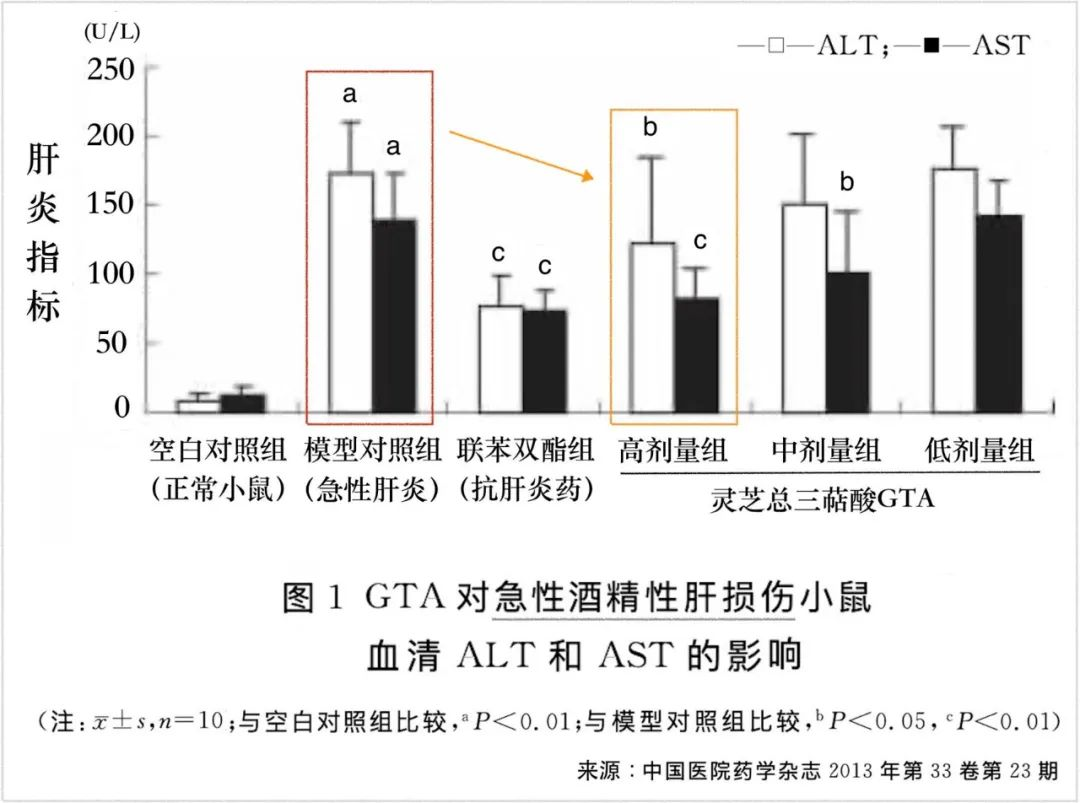
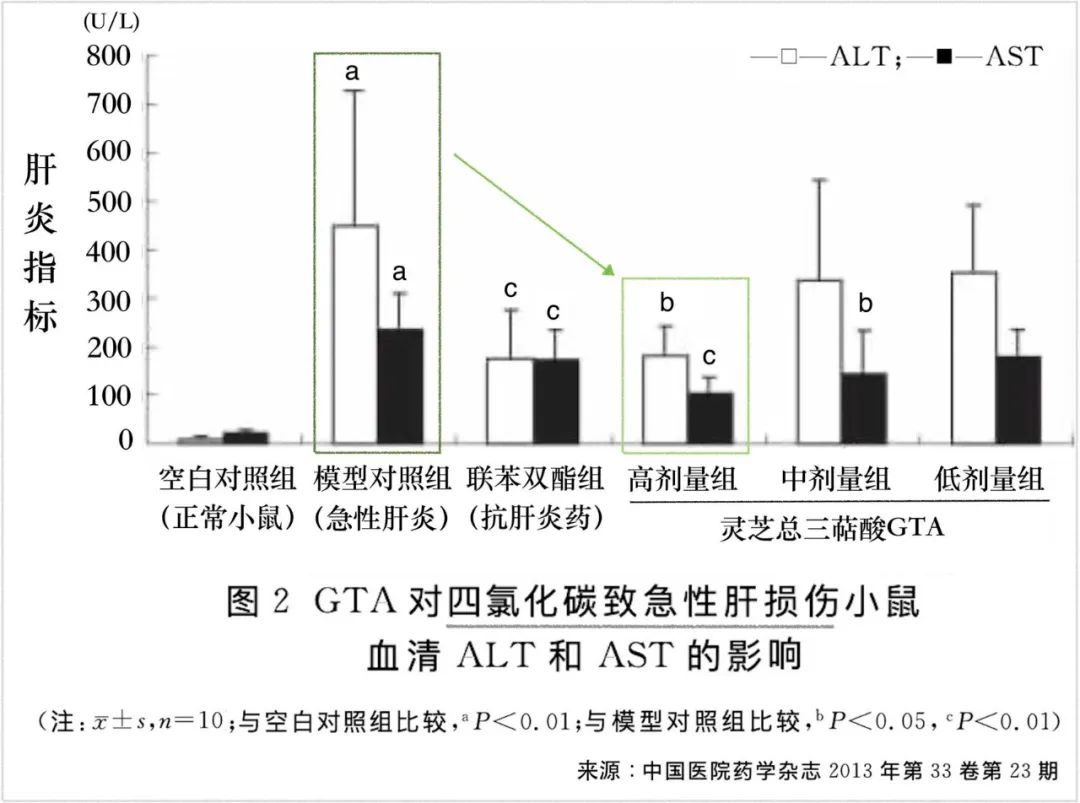
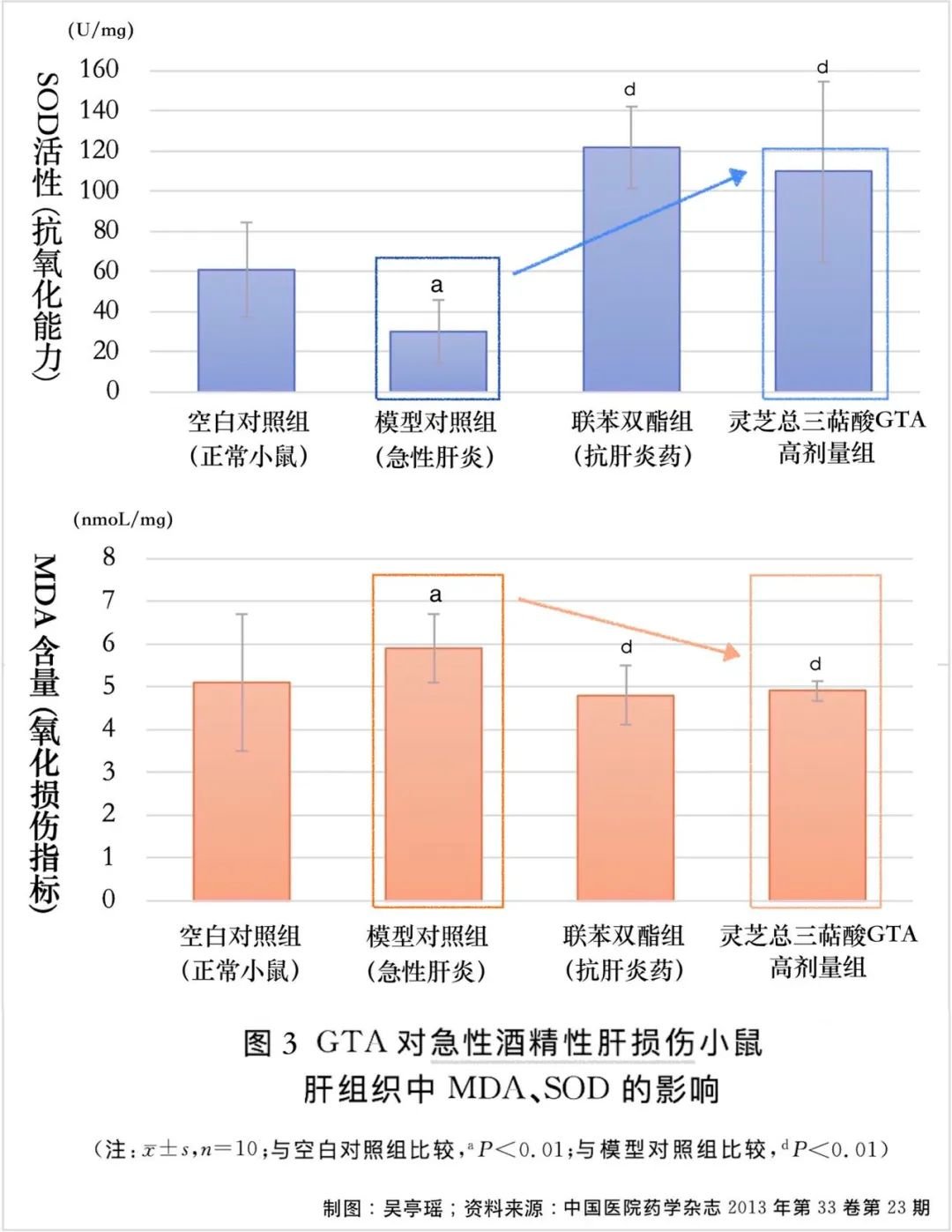
Discovery 2: GTA enhances the liver’s antioxidant capacity.
Why does GTA have a mitigating effect on liver damage? According to the data from this study, mice pre-treated with high doses of GTA exhibited higher levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and lower levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) when faced with damage from Baijiu or carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). SOD can neutralize free radicals, protecting cells from damage, and is a manifestation of antioxidative capacity; MDA is a lipid peroxide generated by free radical attack on cell membranes, reflecting the extent of cellular oxidative damage. Therefore, the increase in SOD and decrease in MDA suggest that the ability of Ganoderma triterpene acids (GTA) to alleviate liver inflammation caused by Baijiu and CCl4 is closely related to the "enhancement of liver cell antioxidative capacity."

Discovery 3: Under GTA protection, there are fewer hepatic tissue lesions.
To gain a more specific understanding of the protective effect of Ganoderma triterpene acids (GTA) on the liver, researchers further examined the extracted liver tissues from mice and provided the following assessments:
- The liver tissues of the blank control group (normal mice) appeared reddish-brown with smooth surfaces, soft texture, and sharp edges.
- The liver tissues of the two model groups (mice with acute liver injury induced by alcohol or carbon tetrachloride) exhibited significantly increased volumes upon gross observation, appeared tan-yellow in color, showed white spots on the surface, had relatively brittle texture, and had dull edges.
- The sizes and colors of the liver tissues observed in the various GTA dosage groups (mice with acute liver injury protected by Ganoderma triterpene acids) fell between those of the model groups and the blank control group.
- Histopathological sections also revealed significant reduction in liver cell lesions in the GTA-treated group.
Based on the comprehensive observation of liver outcomes, coupled with data on serum hepatitis indicators and liver tissue oxidative indicators, the researchers finally conclude that GTA has a certain protective effect against acute liver injury induced by Baijiu and carbon tetrachloride. Its mechanism of action is associated with GTA's ability to protect liver cells through antioxidation.
Ganoderma lucidum has protective effects against viral, chemical, and alcoholic liver injuries.
The hepatoprotective effects of Ganoderma lucidum have been known for quite some time, dating back to clinical research conducted as early as the 1970s. However, during that period, liver infections primarily resulted from hepatitis viruses. Consequently, the conclusion drawn was that standalone consumption of Ganoderma preparations or their concurrent use with conventional hospital medications could generally lead to improvements in liver indicators and related symptoms in patients with viral hepatitis within 1 to 3 months.
Today, in addition to viral hepatitis, we face an increasing prevalence of alcoholic liver disease and chemical-induced liver injury due to alcohol consumption and medication. Fortunately, Ganoderma lucidum continues to exhibit significant protective effects against these latter conditions. Among its bioactive components, Ganoderma triterpene acids found in the alcohol extract of Ganoderma lucidum fruiting bodies serve as a potent source of its efficacy. In our modern lives, where medication and alcohol consumption are often unavoidable, safeguarding our liver health becomes crucial. Based on the aforementioned research, daily supplementation with sufficient Ganoderma triterpene acids appears to be a worthwhile strategy for mitigating the liver damage caused by alcohol and medications. Remember, protecting your liver ensures that your liver can protect you.
Reference
Li, P., et al. Protective effects of Ganoderma triterpene acids on acute liver injury in mice. Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy, 2013, 33(23), 1914-1918.

END
★ This article is exclusively authorized by the author for publication, and its ownership belongs to GanoHerb.
★ The above works cannot be reproduced, excerpted or used in other ways without the authorization of GanoHerb.
★ Those who have been authorized to use the works should use them within the scope of authorization and indicate the source: GanoHerb.
★ GanoHerb will pursue legal responsibilities against those who violate the above statement.
★ The original manuscript of this article was authored in Chinese by Wu Tingyao and subsequently translated into English by Alfred Liu. In the event of any inconsistencies between the English translation and the original Chinese text, the latter shall take precedence. For any queries, please reach out to the original author, Ms. Wu Tingyao.


Search
GanoHerb Group
Headquarters Address: Building 9, Phase 1, Innovation Park, Haixi Park, Fuzhou High-tech Zone, Fuzhou City, Fujian Province, China
Healthline:400-8899-773 Hotline:18105908051
COPYRIGHT © GanoHerb Group 闽ICP备05002116号-10 Powered by:300.cn

官方公众号

Wechat Mall

Tmall

Jingdong Mall


